Managing localized messages via backoffice
Introduction
There is a well-known mechanism for internationalization (i18n) in Java known as resource bundles. They contain locale-specific resources, as usual, a file per the language version. Hybris uses the following naming convention for the files used as resource bundles: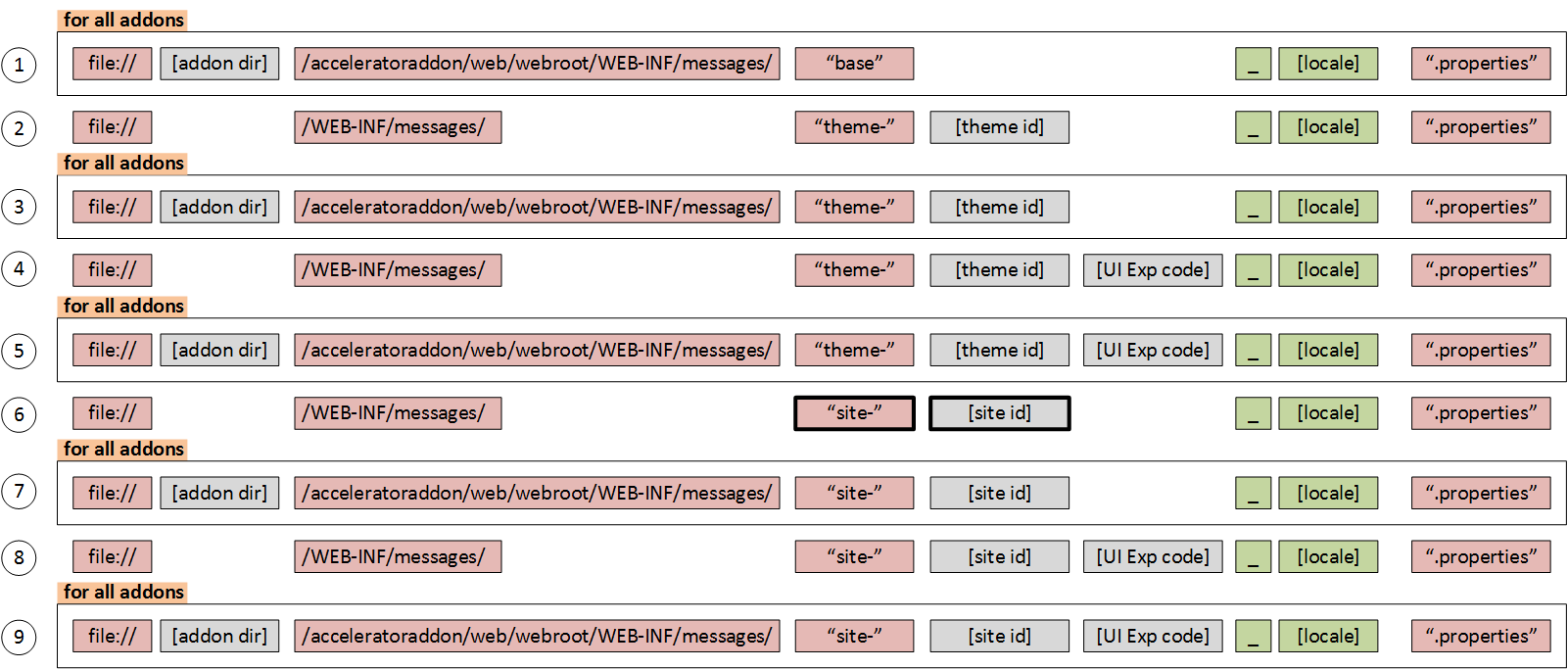 There are different families of the bundles for different websites and add-ons. Each resource bundle in the family contains the same items, but the items have been translated for the locale represented by that resource bundle. Those are key/value pairs. The keys uniquely identify a locale-specific object in the bundle.
Hybris uses this concept for system messages, labels, button titles used in the templates to make them dependent on some website state, such as the language version.
Bundle properties are named after the contents they are supposed to describe. There is a convention to use dot-separated words. For example,
There are different families of the bundles for different websites and add-ons. Each resource bundle in the family contains the same items, but the items have been translated for the locale represented by that resource bundle. Those are key/value pairs. The keys uniquely identify a locale-specific object in the bundle.
Hybris uses this concept for system messages, labels, button titles used in the templates to make them dependent on some website state, such as the language version.
Bundle properties are named after the contents they are supposed to describe. There is a convention to use dot-separated words. For example,
There are more than 2000 items used mainly in templates. Some of the items are used directly from the Java code. There are many of them that are not used at all.
 Using CMS you can change page components, their parameters, but these messages are not editable. If you need to change them, you need to ask the developers, because these files are part of the codebase. It can be said that these messages are hard-coded. It is good that all of them are in the same place and tagged, but the truth is that they are not editable by administrators.
If you find a shameful typo when your website is up and running, it can take hours to fix that. From the technical perspective, there is no a big difference between fixing a minor bug in the code and a typo in the resource files. In both cases, you need to create a patch and apply it to the cluster.
That is why some of my clients are asking to move the messages from the file system to the database to make them editable.
In addition to that, managing the localized messages is very convenient for the translators.
For example, some design elements may not be suitable for the translated text if it much longer or shorter than the original version. For example, there is a property named
Using CMS you can change page components, their parameters, but these messages are not editable. If you need to change them, you need to ask the developers, because these files are part of the codebase. It can be said that these messages are hard-coded. It is good that all of them are in the same place and tagged, but the truth is that they are not editable by administrators.
If you find a shameful typo when your website is up and running, it can take hours to fix that. From the technical perspective, there is no a big difference between fixing a minor bug in the code and a typo in the resource files. In both cases, you need to create a patch and apply it to the cluster.
That is why some of my clients are asking to move the messages from the file system to the database to make them editable.
In addition to that, managing the localized messages is very convenient for the translators.
For example, some design elements may not be suitable for the translated text if it much longer or shorter than the original version. For example, there is a property named
checkout.multi.paymentMethod.addPaymentDetails.generalError
general.month.january
popup.cart.showing
Solution
The extension I would like to introduce pulls the messages from the database instead of the filesystem. It also allows administrators to manage the localized properties using the backoffice interface. All changes are immediately applied to the storefront. The important feature of this solution that it is fully compatible with the existing templates.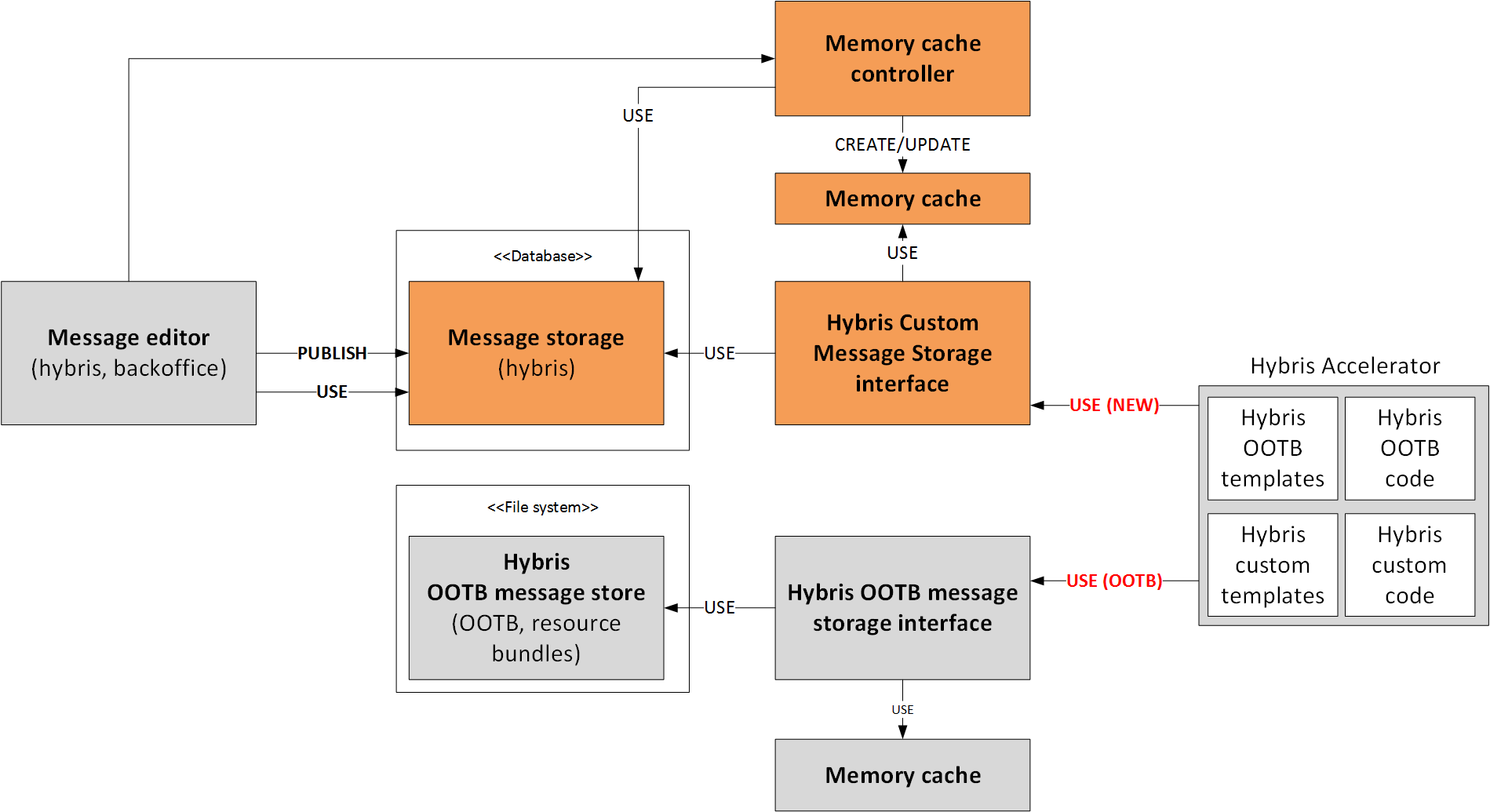
Screenshots
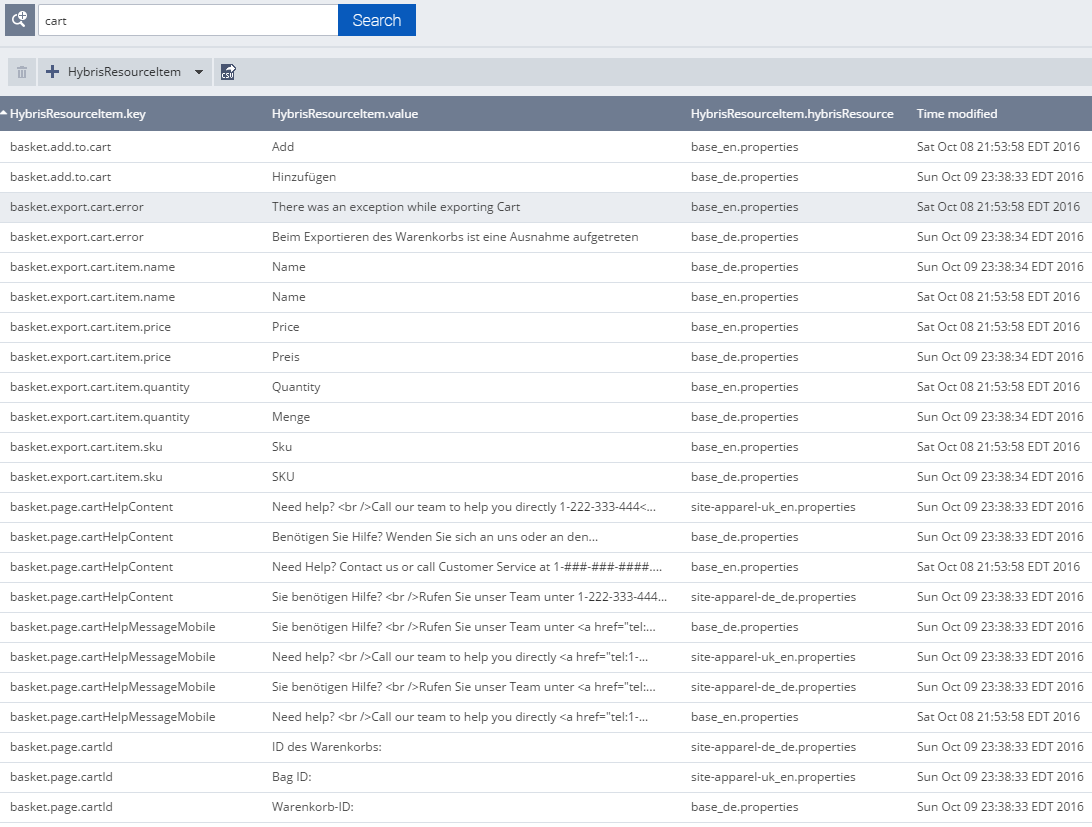
Technical details
- Messages are in the database now. There is a key/value list in hybris, a new object called HybrisResourceItem, and a backoffice extension to work with the object data (key/value/storage).
- There is a storage that plays the same role as a property file does for the file system. Storage is used to group the key/value items. The same key can be created in the different storages. Different language versions or different websites are different storages. There is an object named HybrisResource for the If your e-shop uses 10 different property files, you will have 10 records in the HybrisResource.
- There is a memory cache for the messages to speed up the retrieval. The memory cache is implemented as a simple Map, key->storage content. This cache is invalidated each time you change the HybrisResourceItem.
- There are two large components of the solution:
- New resource management module:
- Extends the spring resource management module (replaces built-in property management with the one that uses hybris services)
- Synchronization:
- Async event-based synchronization
- HybrisResourceItem -> HybrisResource (async merging key-value items into a storage item to speed up a retrieval)
- HybrisResource -> HybrisResourceItem (async splitting the storage item into key-value items)
- Sync synchronization
- HybrisResource -> Memory Cache (if not cached before or when the cache was invalidated)
- Async event-based synchronization
- New resource management module:
HybrisResourceLoader
public class HybrisResourceLoader extends DefaultResourceLoader implements ResourceLoader {
Map<String, Resource> resourceCache = new HashMap<>();
@Override
public Resource getResource(String s) {
Resource resource = getResourceFromCache(s);
if (resource == null) {
Resource hybrisMessageResource = getResourceFromHybris(s);
addResourceToCache(s, fileresource);
...
}
...
}
}
private addResourceToCache(String s, Resource resource ) { resources.add(s, resource) }
private getResourceFromCache(String name) { return resources.get(s); }
private getResourceFromHybris(String s) { ... }
public clearCache (String name)
}
HybrisReloadableResourceBundleMessageSource
public class HybrisReloadableResourceBundleMessageSource extends ReloadableResourceBundleMessageSource {
@Resource
HybrisResourceLoader hybrisResourceLoader;
HybrisReloadableResourceBundleMessageSource(){
super.setResourceLoader(hybrisResourceLoader);
}
public void setResourceLoader(ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
super.setResourceLoader(hybrisResourceLoader);
}
}
HybrisStorefrontResourceBundleSource
public class HybrisStorefrontResourceBundleSource extends StorefrontResourceBundleSource {
@Resource
HybrisResourceLoader hybrisResourceLoader;
protected AbstractMessageSource createMessageSource(final String basename)
{
ReloadableResourceBundleMessageSource messageSource = (ReloadableResourceBundleMessageSource) super.createMessageSource(basename);
messageSource.setResourceLoader(hybrisResourceLoader);
return messageSource;
}
}
HybrisResourceUpdatedEventListener
public class HybrisResourceUpdatedEventListener extends AbstractEventListener {
static final private Logger LOG = Logger.getLogger(HybrisResourceUpdatedEventListener.class);
@Autowired
HybrisResourceLoader hybrisResourceLoader;
@Override
public void onEvent(final HybrisResourceUpdatedEvent event)
{
hybrisResourceLoader.clearCache(event.getName());
}
}
© Rauf Aliev, October 2016


Three things that every hybris project should consider | hybrismart | SAP hybris under the hood
16 November 2016 at 21:55
[…] The solution of the most listed issues is similar to explained in one of my previous posts, “Managing localized messages in Backoffice” […]
Julio Argüello
24 November 2016 at 03:43
Interesting topic, we have implemented a similar solution.
One important thing to take into account is cache invalidation at cluster level. A ClusterAwareEvent whose listener just “refresh” the resource bundle does the trick.
Another related topic is how does Hybris implements resource bundle hierarchy, in some cases it is too deep (mainly when addons are in place) and most of time the key is retrieved from the last bundle: this worst case is most of times the most frequent case… …so a lot of contention appear during stress tests…
Rauf Aliev
27 November 2016 at 08:43
Thank you, very useful points. It would be interesting to see at the performance tests to understand a level of impact of this piece of these system..